HOW SHOULD YOU START?
I asked the above question to myself, and here is my strategy to succeed as an HR Director, which is based on a strategic approach that emphasizes four key elements to propel organizational success. In order to evaluate the present status of the business’s HR professionals should pinpoint the advantages, disadvantages, and potential areas for development first, I will start with a thorough HR audit, making well-informed decisions based on logic and data. To guarantee an integrated and progressive approach, I will then concentrate on developing HR strategies and coordinating HR goals with the organization’s overarching business objectives. In the same lines, I will encourage staff involvement and obtain insightful data, I will use surveys as a tool. opinions of employees will be a top priority for me in order to make sure their suggestions are heard and taken into consideration. Lastly, I will take the lead in developing HR procedures and policies that are equitable, transparent, and in line with industry best practices, guaranteeing uniformity and effectiveness throughout the company. By taking these actions, I hope to create a strong HR foundation and policies that promote worker happiness.
Starting as an HR Director – First thing to do
- START WITH AN HR AUDIT.
Know the Present Situation of the Business: Start by doing an extensive HR audit to evaluate the HR operations of the business as they stand now. These cover assessing present systems, policies, and procedures.
- Key Areas to Audit:
- HR Structure: Review the present HR staff, roles, and responsibilities in key areas of the audit.
- HR Processes: Evaluate recruitment, onboarding, employee development, performance management, and retention plans under HR processes.
- HR Metrics: Analyze important HR numbers, including employee engagement, turnover rates, and time-fill open positions.
- Corporate Culture: See how closely the company’s declared values match the real working culture, and what is wrong.
- Employee Value Proposition: Estimate the company’s appeal to present and future workers based on its EVP, (Employee Value Proposition).
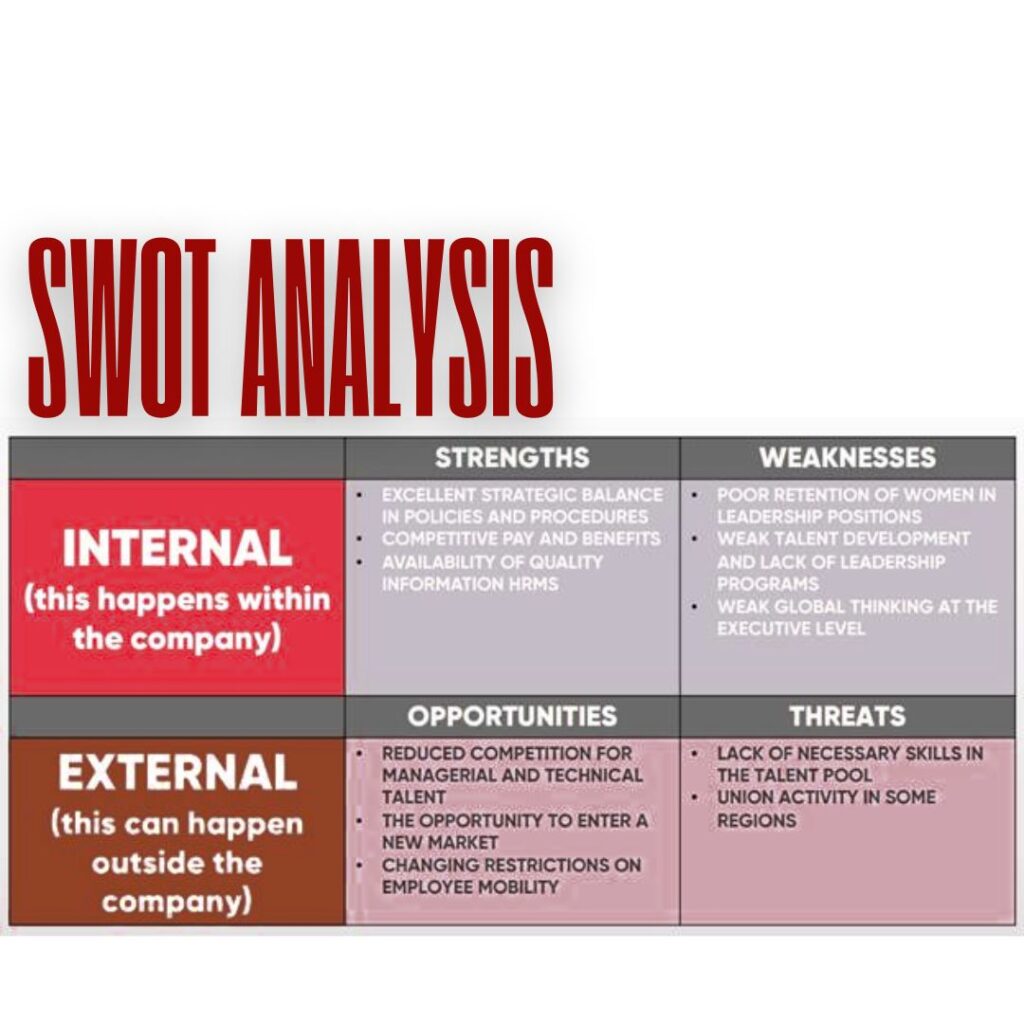
- SWOT Analysis: Conduct a SWOT analysis to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to HR, this will work as a clear guideline and as road map.
- PESTEL Analysis: Analyze outside elements (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, Legal) that could affect HR strategies PESTEL analysis.
- Actionable Insights: Your HR strategy will be informed by the identification of holes and areas for development found by the audit results.
- HR STRATEGY DEVELOPMENT
- Aligning HR with Business Goals: Create an HR plan that complements the overarching business goals of the organization. Make ensuring that HR efforts align with the mission, vision, and values of the organization.
- Strategic Projects:
- Talent Acquisition: Pay close attention to luring and keeping top talent, particularly in markets with fierce competition.
- Employee Development: Put in place initiatives for lifelong learning and professional advancement.
- Performance Management: To guarantee alignment with business objectives, implement or improve performance management systems such as OKRs (Objectives and Key Results).
- Diversity & Inclusion: To encourage creativity and worker satisfaction, cultivate a varied and inclusive workplace.
- HR Roadmap: Create a thorough and extensive HR roadmap with a few short- and long-term goals that come with the timetable and who is doing what.
- Budgeting: Ensure that HR initiatives are sustainable by allocating resources effectively; determine all necessary calculations applied to know the ROI of the initiative.
- Change Management: In case the audit produces significant gaps or problems, the initiative will be fully prepared to lead in organizational change.
3. CONDUCTING EMPLOYEE SURVEYS
- See Employee Needs: Conduct regular employee surveys to gauge satisfaction, engagement, and areas of concern. Use tools like eNPS (Employee Net Promoter Score) and engagement surveys.
- Key Survey Areas:
- Job Satisfaction: Measure how satisfied employees are with their roles, work culture, and responsibilities.
- Engagement: Assess the level of employee engagement and identify factors that contribute to or hinder engagement.
- Well-being: Evaluate employee well-being, including work-life balance, mental health, and physical health.
- Feedback on Management: Gather feedback on leadership effectiveness and management practices.
- Action-oriented Feedback: Use results from surveys to identify trends, voice of staff for improvements. Share findings with management and create action steps to address concerns on a monthly basis.
- Continuous Improvement: Conduct regular employee surveys to measure and track satisfaction and engagement with a continuous improvement mindset. This is also helpful in coping with change management.
4. CREATION OF HR POLICIES AND PROCESSES
- Developing detailed HR Policies:
- Employee Handbook: The Employee handbook should be either be newly written or updated as per recent HR trends to ensure they communicate policies, rules, benefits, and expectations for all employees clearly.
- Code of Conduct: Establish a code of conduct that outlines ethical standards and acceptable behavior in the workplace as per company goals.
- Work Rules: Define clear rules for day-to-day administration and operations to ensure consistency and fairness among all staff.
- Standard Operating Procedures Implementation (SOPs):
- Recruitment and Onboarding: Develop advanced and standardized processes for hiring, onboarding, development and integrating new employees.
- Performance Management: Create easy and clear procedures for setting goals, conducting performance reviews, and providing feedback.
- Employee Development: Set up processes to identify training needs, develop individual development plans and maintain follow-up on progress.
- Compliance and Legal Considerations: The development of HR policies and processes should ensure compliance with local labor laws and regulations. In addition, policies shall be consistently reviewed to ensure their remote alignment with changes in legislation.
- Communication and Training: Communication with all employees regarding new or updated policy is undertaken, together with training to ensure that everyone understands the policy and complies with it.
- Feedback Loop: Create mechanisms for employees. See, there is a right format for all employees to give feedback on any HR policy and/or process to make sure that they remain relevant and effective.
Article Submitted by By: Dr. Zohaib Azhar, BOD Alumni Association EIU-Paris on 12.03.25
𝗖𝗼𝗻𝘁𝗮𝗰𝘁:
📩 [email protected]
📞WhatsApp: +33607591197
🌐 https://eiu.ac/lead_form/
𝗦𝗼𝗺𝗲 𝗨𝘀𝗲𝗳𝘂𝗹 𝗣𝗮𝗴𝗲𝘀:
📑 Journals Library https://eiu.ac/journals/
✍️ EIU-Paris Blogs https://blog.eiu.ac
🎦 Workshops https://www.eiuworkshops.com
🎓 Merchandise https://shop.eiu.ac/
📔 Magazine https://blog.eiu.ac/eiu-magazine/
🎓 Alumni https://alumni.eiu.ac/community

